
The Basics
We Explore several topics in detail, including-
Definitions of A.I. and natural language processing, use cases and common practices, the history of A.I., early pioneers, legacy models, international efforts, what the heck is “All we need is attention”, Image Generation, Video Generation



A.I. 101
A complete foundational guide to Artificial Intelligence
1) What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the field of building machines that can:
- Perceive information (text, images, audio, data)
- Learn patterns from examples
- Reason or make decisions
- Act toward goals
Modern AI does not “think like a human.”
It models patterns statistically and applies them at scale.
2) Why AI exists (the real motivation)
AI exists because:
- Humans are slow at scale
- Data volume exceeds human cognition
- Many problems are pattern-heavy, not rule-based
- Computers can optimize, predict, and simulate faster than people
AI is best at:
- Repetition
- Pattern recognition
- Optimization
- First-pass reasoning
- Assistance and augmentation
Humans remain best at:
- Judgment
- Ethics
- Meaning
- Creativity (direction, not execution)
- Responsibility
3) A short history of AI
1950s — The birth
- Alan Turing
- Proposed the Turing Test
- Asked: “Can machines think?”
1956 — The name “Artificial Intelligence”
- John McCarthy
- Coined the term Artificial Intelligence
1960s–1970s — Symbolic AI
- Logic, rules, expert systems
- Worked only in tiny, controlled domains
1980s — Expert systems boom (and bust)
- Hard-coded rules became unmaintainable
1990s–2000s — Machine learning
- Statistical models learn from data
- Spam filters, recommendations, forecasting
2010s — Deep learning
- Neural networks scale with data + GPUs
- Big wins in vision, speech, language
2017–present — Foundation models
- Transformers enable modern AI
- One model, many tasks
4) Early pioneers you should know
- Alan Turing — computation & intelligence
- John McCarthy — AI as a field
- Marvin Minsky — symbolic AI
- Geoffrey Hinton — neural networks
- Yann LeCun — convolutional networks
- Yoshua Bengio — representation learning
5) What is “All You Need Is Attention”?
Attention Is All You Need introduced the Transformer.
In simple terms:
Instead of reading words one-by-one, the model:
- Looks at all words at once
- Decides what matters most
- Weighs relationships dynamically
This is called attention.
Transformers power:
- Chatbots
- Code assistants
- Image generation
- Video generation
- Search
- Agents
“All You Need Is Attention”
The paper that changed Artificial Intelligence
5a) What is “All You Need Is Attention”?
Attention Is All You Need is a landmark research paper published in 2017 by researchers at Google.
It introduced the Transformer architecture, which:
- Removed recurrence (RNNs)
- Removed convolution (CNNs)
- Used attention alone to model sequences
This single idea became the foundation of:
- Modern language models
- Image generation
- Video generation
- Multimodal AI
- Agents and copilots
5b) Why the paper mattered (the core breakthrough)
Before this paper, sequence modeling relied on:
- RNNs / LSTMs → slow, sequential, poor long-range memory
- CNNs → limited context windows
The paper proved:
You don’t need recurrence or convolution to understand sequences.
You only need attention.
This allowed models to:
- Process entire sequences in parallel
- Learn long-range relationships
- Scale dramatically with data and compute
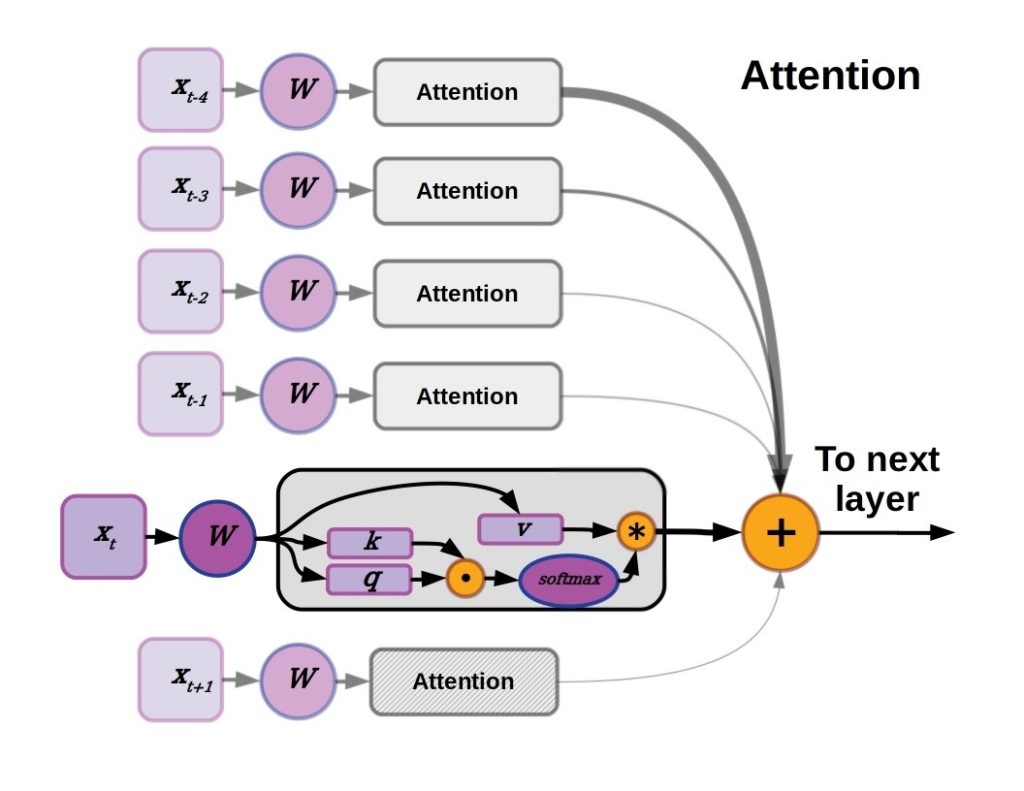
5c) What “attention” actually means (plain language)
Attention answers one question:
“Which parts of the input matter most right now?”
For every token (word, pixel, patch), the model:
- Looks at all other tokens
- Assigns importance weights
- Combines information based on relevance
This happens dynamically, not via hard rules.
5d) The math intuition (without equations)
Each token creates three vectors:
- Query (Q) – what am I looking for?
- Key (K) – what do I contain?
- Value (V) – what information do I provide?
The model:
- Compares Q to all K
- Computes similarity scores
- Turns scores into weights
- Uses weights to mix V
That weighted mixture becomes the token’s new representation.
5e) Self-attention vs traditional sequence processing
| Method | Limitation |
| RNN | Must process tokens one-by-one |
| LSTM | Long-range memory still weak |
| CNN | Fixed context window |
| Self-Attention | Global context, parallel |
Self-attention sees everything at once.
5f) Multi-Head Attention (why one attention isn’t enough)
Instead of one attention mechanism, Transformers use multiple heads.
Each head learns:
- Syntax
- Semantics
- Positional relationships
- Entity references
- Long-range dependencies
Think of it as:
Several specialists looking at the same sentence from different angles
The results are combined into a richer understanding.
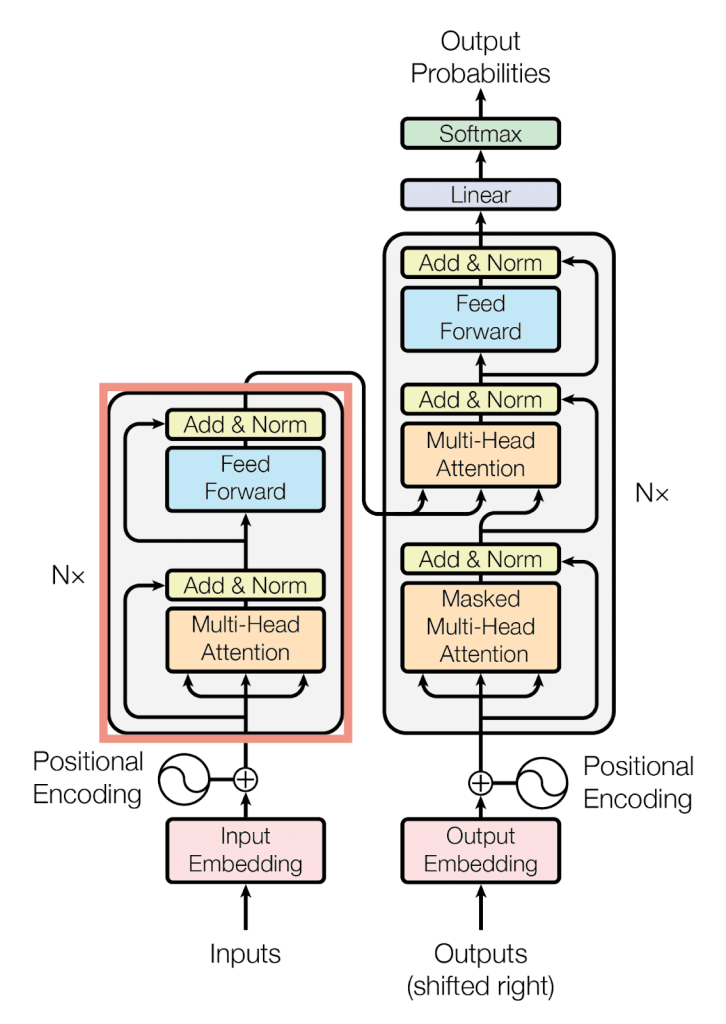
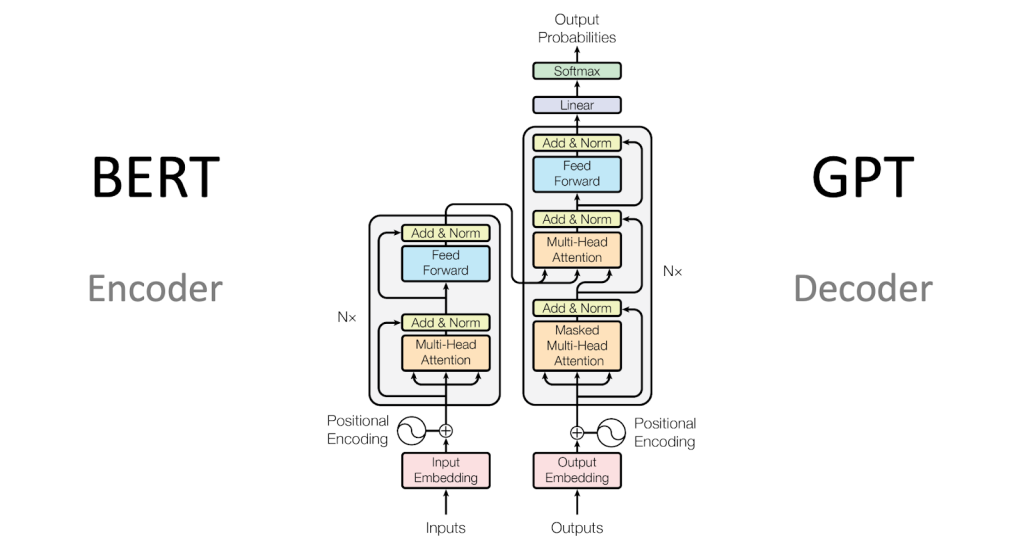
5g) Transformer architecture (high-level)
A Transformer has two main parts:
Encoder
- Reads input
- Builds contextual representations
Decoder
- Generates output
- Uses masked attention so it can’t see the future
Each block contains:
- Multi-head self-attention
- Feed-forward neural network
- Residual connections
- Layer normalization
This stack is repeated many times.
5h) Why Transformers scale so well
Transformers:
- Parallelize perfectly on GPUs
- Improve predictably with scale
- Benefit directly from more data
This led to:
- Bigger models
- Longer context windows
- Emergent abilities
Which explains the explosion of modern AI.
5i) How this paper enabled modern AI systems
Direct descendants include:
- Chat systems
- Code assistants
- Search engines
- Image generators
- Video generators
- Autonomous agents
Even diffusion models and vision transformers rely on attention internally.
5j) “All you need is attention” — the deeper meaning
The title is intentionally provocative.
It doesn’t mean:
“Nothing else matters”
It means:
Attention is the core operation from which intelligence can emerge.
Everything else:
- Memory
- Reasoning
- Creativity
- Multimodality
Is built on top of attention.
5k) Common misconceptions
❌ Attention = memory
❌ Attention = reasoning
❌ Transformers “understand” language
✅ Attention = relevance weighting
✅ Understanding is emergent, not explicit
✅ Reasoning is approximated through structure + scale
5l) Why this paper is taught in every AI curriculum
Because it:
- Unified NLP architectures
- Simplified model design
- Enabled unprecedented scaling
- Changed how researchers think about intelligence
There is a clear before and after this paper.
5m) Lasting impact (in one sentence)
“Attention Is All You Need” transformed AI from handcrafted sequence models into scalable, general-purpose intelligence engines.
6) Local AI vs Cloud AI (important distinction)
Cloud AI
Runs on remote servers.
Pros
- Very powerful
- Always updated
- Handles huge models
Cons
- Cost
- Latency
- Privacy concerns
- Internet required
Local AI
Runs on your device.
Pros
- Privacy
- Offline
- Low latency
- Predictable cost
Cons
- Smaller models
- Hardware limits
Reality (most systems)
Hybrid
- Local AI for filtering, privacy, speed
- Cloud AI for heavy reasoning
7) What are “models”?
A model is a trained mathematical system that maps:
input → output
Examples:
- Text → text (chat)
- Text → image
- Image → text
- Video → video
- Audio → text
8) Major categories of AI models (AI 101 list)
Language models (LLMs)
- Text understanding and generation
Vision models
- Image recognition, segmentation
Multimodal models
- Combine text, image, audio, video
Generative models
- Create new content
9) Popular legacy & modern models (high level)
Language / Multimodal
- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Meta
Image generation
- Diffusion-based models (text → image)
Video generation
- Frame prediction + diffusion + transformers
10) How image generation works (simple)
Most modern image models use diffusion:
- Start with noise
- Gradually remove noise
- Guided by text embeddings
- Image “emerges”
This is why prompts matter.
11) Video generation (why it’s harder)
Video adds:
- Time
- Motion consistency
- Physics
- Memory
Video models predict:
- Frames
- Motion vectors
- Temporal coherence
This is computationally expensive.
12) International AI efforts (big picture)
- United States — commercial leadership, foundation models
- China — large-scale national investment, local platforms
- Europe — regulation, safety, research depth
- Japan & South Korea — robotics + manufacturing AI
- Canada — deep learning research roots
- UK — safety & frontier model research
AI is now geopolitically strategic.
13) What AI is good at vs bad at (AI 101 truth)
Good at
- Summarizing
- Translating
- Pattern recognition
- Drafting
- Search
- Coding assistance
Bad at
- Truth guarantees
- Moral reasoning
- Long-term planning without guidance
- Understanding consequences
- Replacing human responsibility
14) General best practices (AI 101 safe usage)
For everyone
- Treat AI as assistive
- Verify important outputs
- Don’t share sensitive data blindly
- Ask why, not just what
For builders
- Log outputs
- Add guardrails
- Use retrieval for facts
- Test edge cases
- Keep humans in the loop
15) The most important AI 101 idea
AI is a tool for amplification, not replacement.
It magnifies:
- Skill
- Intent
- Carelessness
- Wisdom
